The difference between lead-acid batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries, which product has more advantages and which product can reduce business costs
Lead-acid batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries are two common battery types with significant differences in chemical composition, performance, cost, service life, etc. Here are their main differences, as well as an analysis of which battery product is more advantageous and cost-effective:
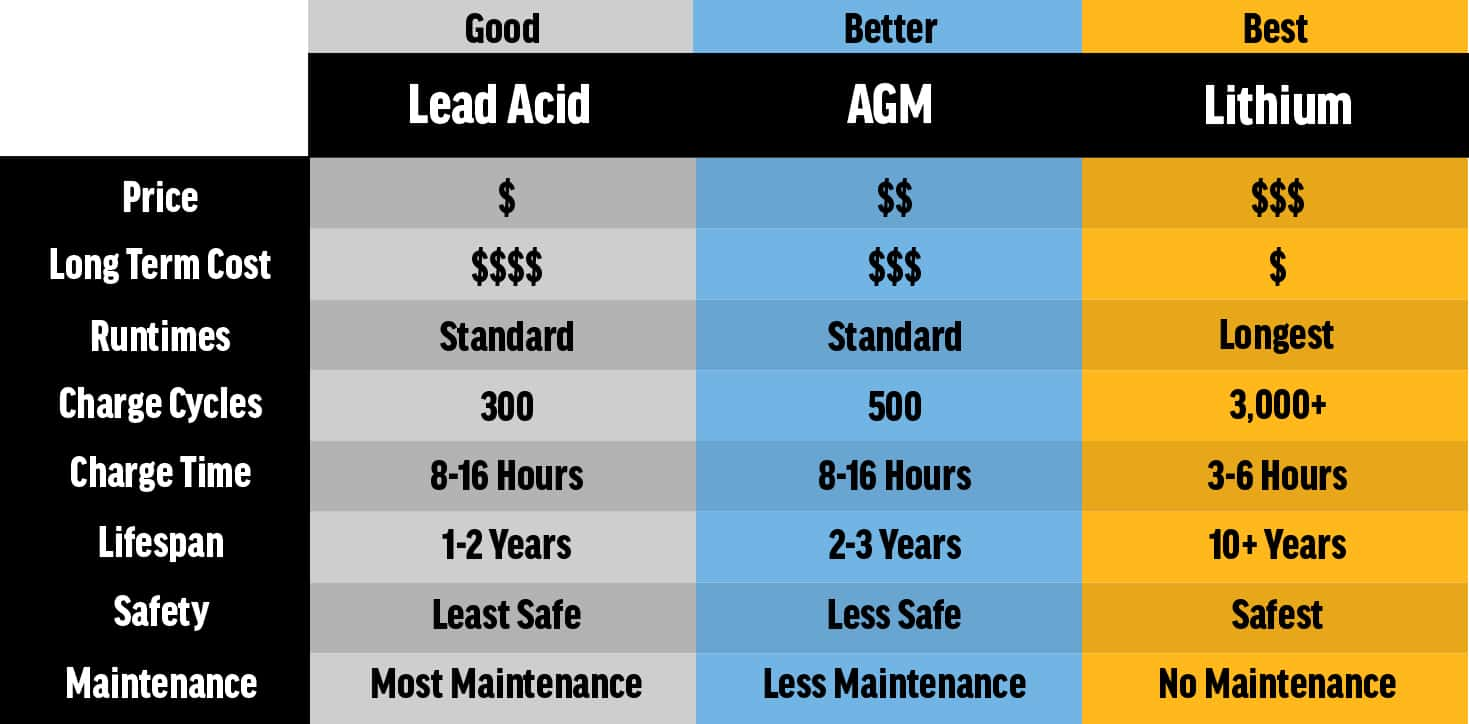
1. Chemical composition and working principle
Lead-acid battery: uses lead and lead oxide as positive and negative electrode materials, and the electrolyte is usually sulfuric acid solution. The working principle of lead-acid batteries is based on the redox reaction of lead.
Lithium iron phosphate battery: uses lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) as the positive electrode material, graphite as the negative electrode material, and the electrolyte is an organic solvent containing lithium salt. Lithium iron phosphate batteries utilize the intercalation and deintercalation processes of lithium ions for charge storage.
2. Performance comparison
Energy density:
Lead-acid batteries: Relatively low energy density, typically 30-50 Wh/kg.
Lithium iron phosphate battery: higher energy density, usually 120-150 Wh/kg. This means that a lithium iron phosphate battery of the same volume and weight can store more electrical energy.
Service life:
Lead-acid batteries: The service life is generally 300-500 charge and discharge cycles, and the performance will decline rapidly over time.
Lithium iron phosphate battery: has a long service life, which can reach 2000-5000 charge and discharge cycles, and has a long service life.
Charging speed:
Lead-acid batteries: charge slowly, usually taking 8-12 hours to fully charge.
Lithium iron phosphate battery: Charging speed is fast, and some high-power batteries can be fully charged within 1 hour.
Security:
Lead-acid batteries: Due to their chemical composition, they are prone to gas generation and can leak or explode when overcharged or short-circuited.

Lithium iron phosphate battery: It has high thermal stability and chemical stability, and is relatively safe when overcharged and short-circuited.
3. Cost comparison
Lead-acid battery: The initial cost is lower, it is a traditional battery type, and the price per unit capacity is cheaper. Suitable for applications that do not require long life and high performance.
Lithium iron phosphate battery: The initial cost is higher, but with the advancement of technology and the increase in production scale, the price gradually decreases. In the long term, despite the higher initial investment, its longer service life and lower maintenance costs may make it more cost-effective in its overall use.
4. Environmental impact
Lead-acid batteries: High lead content, improper disposal after disposal may cause environmental pollution, and recycling is more complicated.
Lithium iron phosphate battery: Lithium iron phosphate battery has less impact on the environment, is rich in lithium and iron resources, and is more environmentally friendly for recycling.
5. Application areas
Lead-acid batteries: Due to their low price, they are often used in low-cost battery applications such as car starting batteries, UPS power supplies, electric bicycles, etc.
Lithium iron phosphate battery: Due to its higher energy density and long life, it is widely used in scenarios with high performance requirements such as electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and solar energy storage equipment.
6. Business cost considerations
From the perspective of reducing business costs:
If a company mainly considers initial investment costs, lead-acid batteries will be more advantageous in the short term because their purchase costs are lower.
If you consider long-term operating costs, such as battery replacement frequency, maintenance costs, etc., lithium iron phosphate batteries have more advantages. Although the initial investment is higher, its longer service life, less maintenance requirements and lower energy consumption can help companies save more costs in the long term.

Comprehensive comparison
Short-term, low-cost option: If your business has a limited budget and doesn’t have high battery life requirements, lead-acid batteries may be a good choice.
Long-term benefit choice: If companies pursue higher reliability, longer service life and lower total cost of ownership, lithium iron phosphate batteries will be a better choice.



